BEING COMPETITIVE IN THE MARKETPLACE

Today’s manufacturers face a host of challenges related to effectively managing product design and manufacturing data. How well manufacturing organizations manage product and production data—and leverage this data to support related functions—has a direct bearing on a manufacturer’s ability to grow, as well as maintain and extend its competitive edge.
As product development and manufacturing organizations increasingly depend on computer-aided digital technologies to design and produce products, the data on which those processes rely has become the lifeblood of these companies. And just as healthy blood flow is an indication of overall fitness and physical performance in human beings, expertly leveraged, utilized, and managed data flow indicates an organization’s fitness to grow, compete, and prosper in today’s global economy.
Manufacturers will enhance competitiveness and benefit from improved data management for a variety of reasons. First and foremost, among these is that improved data management will boost productivity through support of greater automation and organizational efficiencies. Yet the benefits of improved data management extend beyond its capacity to increase productivity and include its ability to improve product quality, facilitate effective collaboration, boost enterprise agility and flexibility, and inspire greater innovation.
The article is an attempt to explore why better data management benefits today’s manufacturing companies by examining the top five reasons why manufacturers should improve their data management function and how they can realize the benefits of Product Data Management (PDM).
Alongside is highlighted how improved data management positively affects the operations of product development and manufacturing departments, as well as how effective data management can benefit every other function across the manufacturing enterprise, particularly through the integration of product data management and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems.
Why manufacturers must improve data management
The top five reasons for manufacturers to improve data management—1) increased productivity, 2) improved product quality, 3) more effective collaboration, 4) enhanced organizational agility and flexibility, and 5) greater innovation—all stem from a manufacturing organization’s ability to manage, secure, find, and leverage product data efficiently and effectively, not just in product development and production but also across the manufacturing enterprise. By improving data management, manufacturing organizations will be able to boost productivity by doing the following:
Automating manual, repetitive tasks – Throughout every manufacturing organization, a myriad of manual, repetitious tasks exert a real drag on productivity—tasks such as the manual creation of bills of materials (BOMs) or revision-checking on drawings. PDM tools can help identify all the manual, repetitive tasks in workflows that can be automated, sped up, or eliminated, boosting productivity while establishing a more accurate, secure process.
Minimizing delays, cost overruns – Missing deadlines and going over budget are clear signs that product development and manufacturing workflows are out of step and can benefit from the workflow automation that a PDM system provides. PDM tools can help manufacturers institute the automated workflows that can resolve time-intensive, costly issues and steps, and make schedule delays and cost overruns a rarity instead of the norm.
The top five reasons for manufac- turers to improve data man- agement all stem from a manu- facturing
organization’s ability to manage, secure, find, and leverage product data effi- ciently and effectively
not just in product development and production, but across the manufacturing enterprise.
Integrating PDM and ERP systems – Many manufacturers rely on a PDM system to manage product development and manufacturing data, and a separate ERP system to manage all other business-related data. By integrating PDM and ERP systems so that they work in concert as a single system, manufacturers can realize additional productivity gains.
Eliminating wasteful, redundant processes – Every manufacturer has legacy processes that were once useful and critical to developing and manufacturing products, but no longer serve any practical purpose. As manufacturers increasingly rely on computer-aided digital technologies to design and produce products, a PDM system can help scrutinize their existing processes and workflows, and then eliminate, replace, or automate outdated processes by utilizing PDM to revamp workflows.
Working smarter instead of harder – Getting more out of existing resources to boost productivity does not necessarily require manufacturers to force staff to work longer, harder hours. An integrated PDM system will enable staff to accomplish more in the same amount of time—not by working harder, but by working more intelligently due to the automation and structure imposed by PDM.
Accelerating time to market – As part of the development, production, and market introduction of all new products, manufacturers lose substantial amounts of time due to confusion, questions, and miscommunications involving data. With a PDM system supporting automated, formalized workflows, manufacturers can winnow out unnecessary instances of lost time and consistently accelerate product time to market.
Achieving additional automation via API – While a PDM system can help a manufacturing organization automate many processes, choosing an integrated PDM system with an open Application Programming Interface (API) carries the potential for automating additional processes, especially those that are unique or custom to its products and manufacturing techniques.
With the greater pro- ductivity, flexibility, and agility provided by a PDM system, manufacturers can more
quickly average broader collabo- ration and more agile operations to inno- vate new products, pursue new markets, or both.
Improve Product Quality
By improving data management, manufacturing organizations will be able to sustain consistently high levels of quality by doing the following:
Eliminating revision errors – Shoddy product quality caused by working with old, out-of-date revisions was common when data management consisted of physically filing paper drawings in cabinets and drawers. With a PDM system’s tighter revision controls, one can eliminate design errors and product issues associated with working with the wrong revision of a product design.
Achieving greater design reuse – Why design a new component when a perfectly good, tested design for the part already exists, buried somewhere in the product data? Of course, if an existing design cannot be found, one cannot reuse it. Data management tools with search capabilities can help a manufacturing organization increase reuse of proven, existing designs. As design reuse grows, product quality improves.
Reducing scrap and rework – Design errors—whether related to use of an out-of-date revision or a new, untested design—have ramifications on a manufacturer’s volume of costly scrap and rework. Any time that a manufacturer needs to rework or retrofit a part or product, the probability that the rework will negatively impact quality grows. A PDM system can help manufacturers weed out revision errors, increase design reuse, and reduce scrap and rework, all of which can help an organization improve product quality.
Improving handling of engineering change orders – When a design or engineering change is required after a product design has already been released for production, manufacturers issue an engineering change order (ECO). How well an organization implements ECOs—and how many ECOs are issued—has a direct bearing on overall product quality. With an integrated PDM system, manufacturers not only can execute ECOs more efficiently but also can ensure that the handling of ECOs produces the result of improving quality.
The benefits of improved data man- agement extend beyond its capacity to increase productivity and include its abilityto improve product quality, facilitate effective collabora- tion, boost enterprise agility and flexibility, and inspire greater innovation.
Facilitate Collaboration
By improving data management, manufacturing organizations will be able to support more effective collaboration by doing the following:
Connecting globally dispersed locations – As manufacturers become more global in scope, the need to connect product development, engineering, and manufacturing groups—as well as related business functions—has become critically important for increasing efficiencies and maximizing resource utilization worldwide. A PDM system with a replicated vault is vital for connecting globally dispersed manufacturing locations and facilitating collaboration among them.
Integrating communications between engineering disciplines and departments – As more and more products include mechanical, electronic, and electromechanical assemblies and components, the need to stimulate and support collaboration between different engineering disciplines and departments is growing. An integrated PDM system can help foster inter-disciplinary collaboration because it establishes a common repository for the design and engineering information required before this type of collaboration can begin.
Linking product development and production – Whenever product development and manufacturing departments are linked by a common PDM system, each department can collaborate more freely and efficiently. Product designers and engineers can collaborate more effectively with production specialists on the best manufacturing method, and manufacturing personnel can see and collaborate over what is coming in the product development queue.
Fostering collaboration with other departments across the enterprise – An integrated PDM system also allows manufacturers to accelerate and support other critical applications that can leverage product design data, stimulating collaboration across the enterprise. Product development information, such as bills of materials (BOMs), development timelines, and anticipated manufacturing processes can then be used to prepare and drive other important functions, including manufacturing planning, estimating, and quoting, purchasing, sales, marketing, and other product launch activities, further streamlining a manufacturer’s core operations.
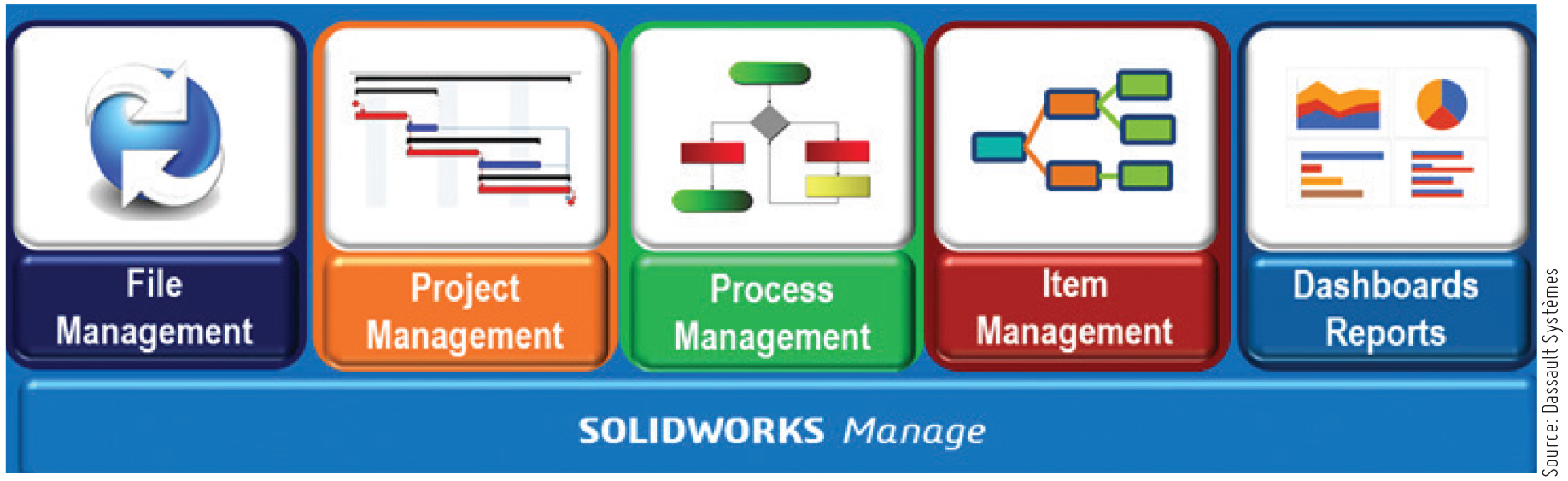
Increase Agility and Flexibility
By improving data management, manufacturing organizations will be able to support increased organizational agility and flexibility by doing the following:
Shortening engineered-to-order lead-times – Shortening development and delivery lead-times is a critical success factor for many manufacturers of engineered-to-order products. The automated workflows supported by an integrated PDM system can dramatically shorten both proposal and product development, giving engineered-to-order manufacturers the agility and flexibility required to compete successfully in a global competitive market.
Incorporating concurrent product development and manufacturing planning – With the agility and flexibility afforded by an integrated PDM system, manufacturing planning can begin concurrently with the final stages of product development. Because both product development and manufacturing personnel can collaborate more effectively during the latter stages of development prior to a product’s release to production, they will need less time to plan for production and have the flexibility to collaborate on and make changes through a product’s release to manufacturing.
Developing products and documentation simultaneously – Instead of waiting until a product is manufactured to develop content for user manuals, service manuals, parts lists, and other forms of product documentation, manufacturers can leverage a PDM system to establish a concurrent workflow through which products and accompanying documentation are developed at the same time, with design changes reflected in auto-updating design data that is used for both purposes.
CP Manufacturing has leveraged the SOLIDWORKS API to automate a host of specific development processes, as well as toautomate manual and repetitive tasks, saving the company considerable time and money.
By implementing additional SOLIDWORKS solutions, including SOLIDWORKS PDM Professional software, Vermeer Corporation has automated its development workflows, increased development and production throughput, shortened and formalized its engineering change process, and improved the quality of its products and documentation.
Inspire Innovation
By improving data management, manufacturing organizations will be able to inspire innovation from within by doing the following:
Including input from across the enterprise – Innovation can come from many places, and some of the best ideas can come from the most unlikely of sources. Innovation does not come from becoming complacent—doing things the way that they have always been done. With an integrated PDM system, manufacturers can gather valuable input and perspectives from across the enterprise, including from those who routinely work with customers and frequently use your company’s products, helping to inspire greater innovation throughout product development.
Leveraging faster, broader collaboration – With the greater productivity, flexibility, and agility provided by a PDM system, manufacturers can more quickly leverage broader collaboration and more agile operations to innovate new products, pursue new markets, or do both. Successfully introducing an innovative product or product feature requires bringing it to market first, and PDM tools can help you move more quickly and decisively than your competitors.
Supporting more-innovative approaches to product development and manufacturing – A PDM system can also help manufacturers support more innovative approaches to product development as well as tap the latest manufacturing techniques. Concurrent product development—whereby all related functions are completed concurrently with the development of a product—and the use of additive manufacturing techniques are examples of the innovative approaches to product development and manufacturing that are supported by PDM.
SOLIDWORKS Solutions
As a leading provider of easy-to-use design, engineering, and product development solutions, SOLIDWORKS has introduced the industry’s first distributed data management product portfolio, which enables manufacturers to take advantage of PDM, advanced data management, and powerful searching applications, either individually or as a combined Distributed Data Management system.
SOLIDWORKS PDM solutions for product data management are fully integrated with increasingly popular SOLIDWORKS design software, enabling manufacturers to safeguard, store, and organize product design data for maximum efficiency. These solutions also allow product development teams to collaborate more effectively. Two different solutions—SOLIDWORKS PDM Standard and SOLIDWORKS PDM Professional—are available, depending on the size and PDM needs of the manufacturing enterprise.
SOLIDWORKS Manage is an advanced data management system that extends the capabilities of the global file management and application integrations enabled by the SOLIDWORKS PDM platform. Combining the ease of use and familiar Windows® Explorer interface of SOLIDWORKS PDM, SOLIDWORKS Manage adds advanced capabilities that allow teams throughout the manufacturing enterprise to manage project timelines and resources, streamline complex business processes, automate records management, and aggregate, communicate, and present PDM-related information in formats tailored for consumption by varied audiences.
Geometry and Metadata Search—EXALEAD® OnePart
EXALEAD OnePart is a business discovery application that accelerates reuse of parts, designs, specifications, standards, test results and related data for engineering, manufacturing, and procurement activities. Leveraging the proven web semantics, analytics, and big data management technologies of EXALEAD CloudView™, OnePart locates information from multiple sources and makes it available instantly.
It extends the text- and file-based search capabilities of SOLIDWORKS PDM solutions into the realm of the 3D shapes, geometries, and mechanical features of existing designs across the entire enterprise. Even without a CAD license, users can search on geometric shape, business function, and even mechanical features, such as holes, pads, and grooves. This application can find parts, drawings, and assemblies, as well as view critical information on parent-child relationships within assemblies, enabling users to navigate down through an assembly to locate a specific part. Part discovery through 3D shape similarity and 3D mechanical feature data mining will reveal existing parts that text- and file-based searches cannot find, facilitating design reuse.
Also, EXALEAD OnePart can quickly locate any type of metadata associated with existing component designs. Metadata search capabilities enable users to discover analysis and testing results, materials and sourcing data, specifications and applicable standards, and price and performance information for any part that is developed anywhere across a manufacturing enterprise.
Leveraging Competitive Strength
By improving their organizations’ ability to manage, secure, find, and leverage product data efficiently and effectively—not just in product development and production, but across the manufacturing enterprise—manufacturers can increase productivity, improve product quality, facilitate collaboration, enhance organizational agility and flexibility, and inspire greater innovation.
A PDM system can help manufacturers weed out revision errors, increase design reuse,
and reduce scrap and rework, all of which can help an organization improve product quality.
Source: Dassault Systèmes, SOLIDWORKS




 Facebook
Facebook.png) Twitter
Twitter Linkedin
Linkedin Subscribe
Subscribe