Navigating Economic Waves
While the Indian economy faces some headwinds, the machine tool industry remains resilient, supported by strong domestic demand and strategic imports.
Article source: Data & Policy Team, IMTMA
The Indian economic outlook for October 2024 exhibits mixed trends across most high-frequency indicators compared to the previous month. The manufacturing PMI dropped to 56.5 in September 24, while services PMI fell to a 10-month low of 57.7, pressured by fierce price increases and weaker growth in new international orders, with export growth hitting an 18-month low. Industrial production IIP declined by -3 percent in September 24, driven by contractions in the Mining and Electricity sectors. The Auto sector registered growth across all segments, fueled by a surge in seasonal demand.
Trade deficit narrows as imports decline
On the trade front, the merchandise trade deficit narrowed to a five-month low in September 24, driven by a significant decline in merchandise imports, particularly gold. Forex reserves hit a record high in September 24, boosted by a notable surge in foreign currency assets and gold reserves. FDI also saw a sharp increase in August 24, primarily directed towards the Manufacturing, Financial Services, Communication, and Energy sectors.
In terms of macroeconomic indicators, WPI inflation rose to 1.84 percent in September 24, driven by a surge in primary article prices. CPI inflation rose to a nine-month high of 5.49 percent, fueled by an 8.4 percent YoY spike in food prices. GST collections saw a modest monthly decline, reflecting subdued economic activity. Consumer confidence improved in RBI’s September 24 survey, with the CSI index rising to 94.7 and the FEI index to 121.4, indicating higher household confidence. IMF has forecasted global growth at 3.2 percent in 2024 and India’s growth at 7.0 percent in 2024.
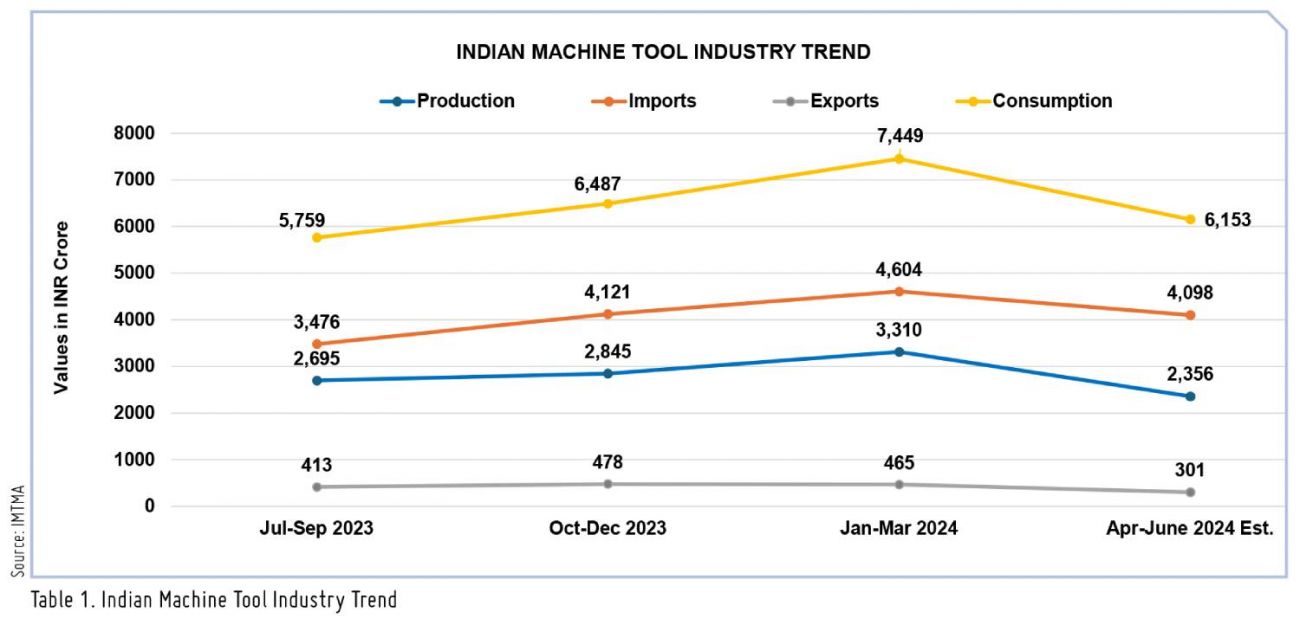
Positive momentum in machine tool industry
The production of the Indian Machine Tool industry in Q1 FY25 is estimated to have increased by approximately 8 percent year-on-year, reaching around INR 2,356 crore (US$ 282 million). The industry’s imports in Q1 FY25 saw a rise of 30 percent year-on-year, amounting to INR 4,098 crore (US$ 491 M). Machine tool exports during Q1 FY25 from India reported a degrowth of 1 percent, amounting to INR 301 crore (US$ 36 M) and consumption is estimated to have increased by about 22 percent to reach INR 6,153 crore (US$ 738 M) in Q1 FY25.
| In exports, Lathes, VMCs, and Presses were the top three machinery exported, valued at INR 262 crore (US$ 31 M) at about 44 percent of total machine tool exports in H1FY25. The total machine tool exports from April to September 2024 (H1FY25) is INR 593 crore (US$ 71 M). |
The total machine tool imports in April to September 2024 (H1FY25) is INR 8,006 crore (US$ 956 M). China (26%), Japan (16%), and Germany (13%) emerged as the top countries for imports, contributing 55 percent of the total machine tool imports in April to September 2024 (H1FY25). Presses, Lathes, and Cylindrical Grinding Machines were the top machinery imported valued at INR 3,038 crore (US$ 363 M) at about 38 percent of total machine tool imports in H1FY25.




 Facebook
Facebook.png) Twitter
Twitter Linkedin
Linkedin Subscribe
Subscribe