Resilience Amid Economic Shifts
Despite economic fluctuations, the Indian machine tool industry is experiencing robust growth in FY25. The Government’s recent budget outlines significant expenditure with a focus on reducing the revenue deficit. Increase in production in Q1 FY25, a rise in imports, and a slight decline in exports. More in the report below.
In July 2024, the Indian Government unveiled its budget for FY25. The budget outlines total expenditure at INR 48.2 lakh crore, split between revenue and capital expenditures in a 77:23 ratio. The budget projected a fiscal deficit to GDP ratio of 4.9 percent. This represents a slight improvement from the 5.1 percent forecasted in the interim budget. A notable highlight is the anticipated enhancement in the quality of the fiscal deficit, with the ratio of revenue deficit to fiscal deficit expected to decrease to 36 percent in FY25, down from 46.3 percent in FY24.
Economic indicators:
PMI and IIP growth
The economic performance indicators for June 2024 reflect a positive trend. The Purchasing Managers' Index (PMI) for both manufacturing and services saw gains, reaching 58.3 and 60.5 respectively, up from 57.5 and 60.2 in May. Additionally, the Index of Industrial Production (IIP) growth accelerated to 5.9 percent in May, driven by increased manufacturing and electricity output, compared to 5 percent in April.
Inflation trends: CPI and WPI analysis
Inflation metrics present a mixed picture. Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation rose to 5.1 percent for the first time since January 2024, although core CPI inflation remained stable at a historical low of 3.1 percent. Conversely, the Wholesale Price Index (WPI) inflation, while still low at 3.4 percent, has been increasing for four consecutive months. This inflationary trend is coupled with an interesting shift in Government finances, with gross tax revenues growing significantly by 15.8 percent in the early months of FY25, driven by robust direct tax collections.
Government spending and fiscal deficit
The fiscal landscape also reveals a contraction in Government expenditure during April-May FY25, with total spending down by 0.4 percent. Revenue expenditure increased by 4.7 percent, but capital expenditure fell sharply by 14.4 percent. Fiscal and revenue deficits for this period were recorded at historically low levels of 3.1 percent and -15.7 percent, respectively. On the banking front, gross bank credit growth remained strong at 16.1 percent in May, up from 15.3 percent in April. In its July 2024 report, the IMF projected global growth rates of 3.2 percent for 2024 and 3.3 percent for 2025. For India, the projected growth rates are 7 percent in 2024 and 6.5 percent in 2025.
Trade and investment dynamics show a slowdown. Merchandise exports and imports grew at 2.5 percent and 5.0 percent in June 2024, down from higher rates in May. The trade deficit narrowed to US$ 21 billion, aided by a decrease in oil imports. Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) inflows eased to US$ 3.3 billion, while Foreign Portfolio Investments (FPI) experienced outflows of US$ 1.5 billion. Globally, crude oil prices dropped to a four-month low of US$ 81.2 per barrel. Economic forecasts from the World Bank and IMF project moderate global growth, with India’s growth expected to range between 6.6 percent to 7.0 percent in the upcoming fiscal years.
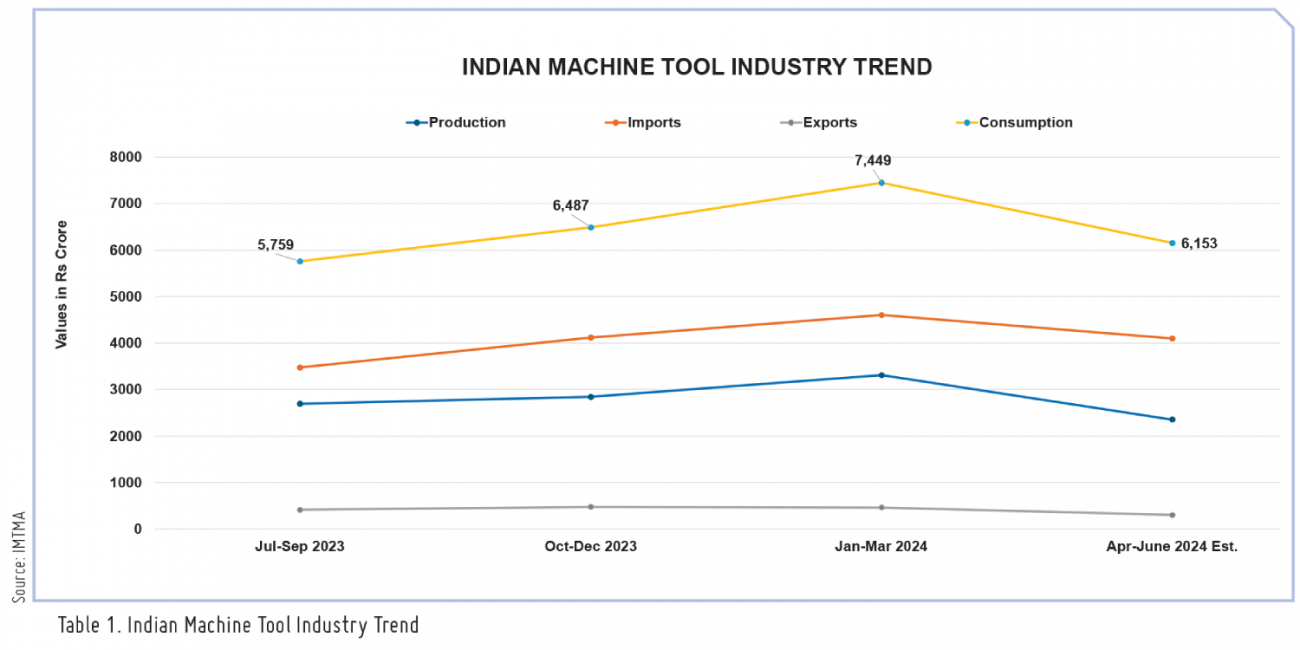
Machine tools production and consumption
The production of the Indian Machine Tool industry in Q1 FY25 is estimated to have increased by approximately 8 percent year-on-year, reaching around INR 2,356 crore (US$ 282 million). The industry's imports in Q1 FY25 saw a rise of 30 percent year-on-year, amounting to INR 4,098 crore (US$ 491 M). Machine tool exports during Q1 FY25 from India reported a degrowth of 1 percent, amounting to INR 301 crore (US$ 36 M) and consumption is estimated to have increased by about 22 percent to reach INR 6,153 crore (US$ 738 M) in Q1 FY25.
|
In Q1 FY25, China (32%), Japan (20%), and South Korea (10%) emerged as the top countries for imports to India, contributing to 62 percent of the total machine tools imports. Presses (15%), Lathes (9%) Cylindrical Vertical Machining Centres (8%) were the top three machinery types imported, valued at INR 1,158 crore (US$ 139 M), constituting about 32 percent of total machine tool imports during the period. Imports from Asian nations like China, Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan contributed 69 percent of total imports during Q1 FY25. In exports, Russia (25%), the UAE (7%), and the US (4%) emerged as the major destinations, collectively representing 36 percent of total machine tool exports in Q1 FY25, amounting to a total export value of INR 301 crore (US$ 36 M). Among the machinery types, VMCs (15%), Lathes (12%), and Cylindrical Grinding machines (7%) stood out as the top three machinery types exported, with a combined value of INR 135 crore (US$ 16 M), accounting for about 34 percent of total machine tool exports during Q1 FY25. |
 |
| In exports, Russia (25%), the UAE (7%), and the USA (4%) emerged as the major destinations, collectively representing 36% of total machine tool exports in Q1 FY25, amounting to a total export value of INR 301 crore (US$ 16 M). |
Article source: Data & Policy Team, IMTMA



 Facebook
Facebook.png) Twitter
Twitter Linkedin
Linkedin Subscribe
Subscribe