CHARTING THE COURSE
India's macroeconomic landscape in March 2024 exhibited promising signs, with manufacturing PMI soaring to a 16-year high of 59.1 and services PMI maintaining a robust position at 61.2 for the third consecutive month.
This surge in economic activity was complemented by a notable increase in Industrial Production (IIP) growth to 5.7 percent in February, fuelled by growth across key sub-industries.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) opted to retain the repo rate at 6.5 percent, marking the seventh consecutive review with no changes. Meanwhile, inflationary pressures exhibited a mixed trend, with CPI inflation easing slightly to 4.9 percent in March 2024, while WPI inflation remained low at 0.5 percent.
On the fiscal front, the Government of India (GoI) witnessed growth in gross tax revenues (GTR) by 13.4 percent during April-February FY24, with direct taxes growing at 21.6 percent, and indirect taxes at 4.6 percent. However, fiscal and revenue deficits remained significant concerns, standing at 86.5 percent and 87.1 percent, respectively, of their annual Revised Estimates (RE).
The Banking sector witnessed a surge in gross bank credit growth to a 16-month high of 16.5 percent in February 2024, while the current account deficit narrowed to 1.2 percent of GDP in 3QFY24. Nonetheless, merchandise trade faced challenges, with both exports and imports contracting in March 2024, leading to a reduction in the merchandise trade deficit to US$ 245.3 billion in FY24.
|
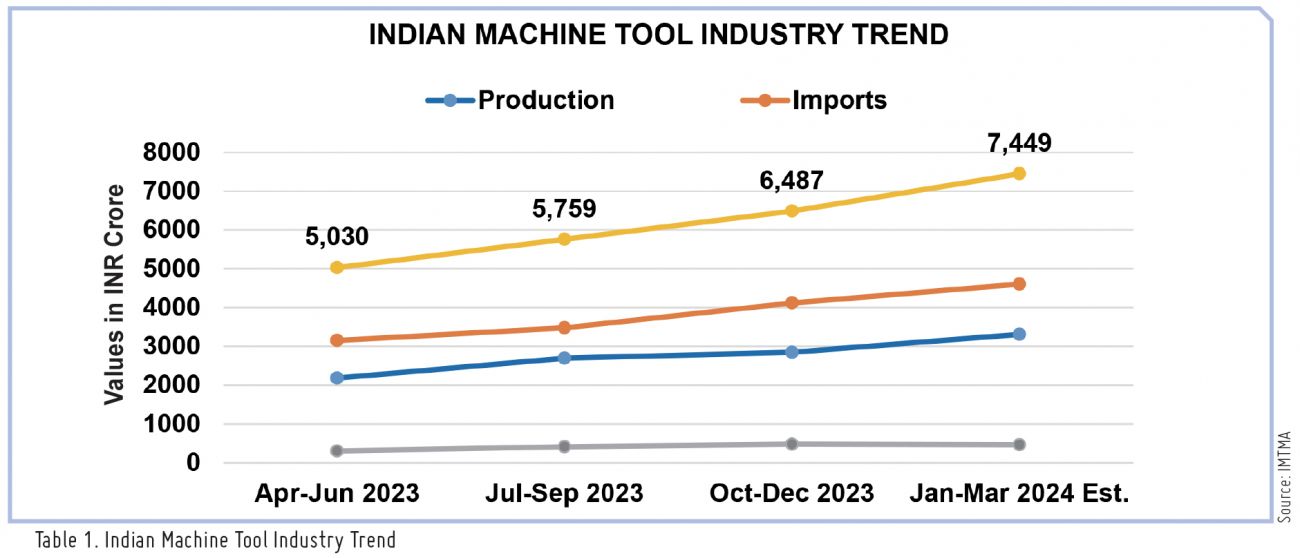
For the second successive year, the Indian Machine Tool industry has achieved double-digit growth. Indian Machine Tool industry production in FY24 is estimated to have increased by around 10% year-on-year, reaching about INR 13,610 Cr. |
FDI inflows experienced a sharp decline to US$ 0.3 B in February 2024, and global crude prices surged to a five-month high of US$ 83.5/bbl. in March 2024. Despite global growth projections remaining steady at 3 percent by the IMF, India's growth forecasts for FY25 and FY26 stand at 6.8 percent and 6.5 percent respectively, showcasing cautious optimism amidst global economic dynamics.
Insights into Indian machine tool sector
Indian Machine Tool industry production in FY24 is estimated to have increased by around 10 percent year-on-year, reaching about INR 13,610 Cr (US$ 1.6 B). The industry's imports in FY24 saw a rise of 12 percent year-on-year, amounting to INR 15,352 Cr (US$ 1.8 B). Machine tool exports during FY24 from India reported a 13 percent growth, amounting to INR 1,659 Cr (US$ 200 M) and consumption is estimated to have increased by about 11 percent to reach INR 27,303 Cr (US$ 3.3 B) in FY24.
In FY24, China (29%), Japan (21%), and Germany (10%) emerged as the top countries for imports to India, contributing to 60 percent of the total machine tools imports. Presses (14%), VMCs (12%), and Turning Centers (11%) were the top machinery types imported, valued at INR 5,700 Cr (US$ 688 M), constituting approximately 37 percent of total machine tool imports during the period.
In exports, Russia (28%), the USA (9%), and China (8%) emerged as the major destinations, collectively representing 45 percent of total machine tool exports in FY24, amounting to a total export value of INR 1,659 Cr (US$ 200 M). Among the machinery types, Turning Centers (17%), VMCs (15%), and Presses (11%) stood out as the top three machinery types exported, with a combined value of INR 705 Cr (US$ 85 M), accounting for roughly 43 percent of total machine tool exports during FY24.



 Facebook
Facebook.png) Twitter
Twitter Linkedin
Linkedin Subscribe
Subscribe