EMBRACING ADAPTIVE AUTOMATION

The evolution of industrial robots towards adaptive automation represents a paradigm shift in manufacturing. It heralds a future where robots are not just tools but intelligent collaborators and contributors, capable of navigating the complexities of modern industry with agility and efficiency.
In the vast landscape of modern industry, a quiet revolution has been unfolding. It's a revolution not led by flesh and blood but by metal and code. Once confined to repetitive tasks within structured environments, industrial robots are now evolving into adaptive automation systems and reshaping the very fabric of manufacturing. This drastic transition not only assures increased efficiency and productivity but also flexibility and resilience that can cater to dynamic demands.
During the early 90s, the rise of industrial robots was triggered by the advancement and technological progress needed to meet the requirements of the Manufacturing industry. Today, industrial robots continue to play an integral role in production lines. Designed for fast and precise position control, these systems are ideal for tasks that require repeated trajectory following, for example, picking and placing an object from a known position to another known position, cutting a particular section of a metal sheet, or spray painting a workpiece. For these repetitive tasks, these robots can support humans for better efficiency, accuracy, and lesser time consumption, thanks to their well-developed hardware and control systems.
With the fusion of advanced robotics, artificial intelligence, and sensor technologies, industrial robots are no longer confined to repetitive tasks; they are increasingly becoming intelligent agents capable of responding to dynamic production environments. They are becoming adaptive and capable of responding to real-time data and adjusting their actions accordingly.
Overview of what defines an Adaptive Robot
Adaptive manufacturing represents a departure from traditional mass production methods where static assembly lines churn out standardized products. Instead, it embraces flexibility, agility, and customization, catering to the demands of an increasingly diverse market. At the heart of adaptive manufacturing lies the ability to quickly adapt and reconfigure production processes in response to changing requirements, market trends, and customer preferences. Industrial robots, equipped with adaptive capabilities, play a pivotal role in enabling this paradigm shift.
One of the key features of adaptive manufacturing is the ability to handle variability in product design and production volume. Thanks to their inherent flexibility and reprogramming ability, industrial robots excel in this regard. Unlike dedicated machinery designed for specific tasks, robots can be easily reconfigured to perform a wide range of operations. Whether it’s welding, painting, assembly, or inspection, robots can seamlessly transition between tasks, allowing manufacturers to adapt to changing production needs with minimal downtime.
The following three main characteristics make the modern robots adaptive:
- Intrinsic safety without compromising on the performance;
- Ability to learn and accomplish new tasks like a fresh trainee engineer;
- Flexibility.
To achieve the goal of adaptivity, the following key features become crucial:
- Force control technology with high accuracy and rapid response;
- Hierarchical intelligence based on vision and force-sensing technology.
|
The evolution of industrial robots towards adaptive automation represents a paradigm shift in manufacturing. It heralds a future where robots are not just tools but intelligent collaborators and contributors, capable of navigating the complexities of modern industry with agility and efficiency. |
MELFA-FR from Mitsubishi
Mitsubishi Electric is a leading maker of factory automation systems and has abundant experience in areas including automotive parts, electronic and electric components, liquid crystal displays, semiconductors, food products, medicines, cosmetic products,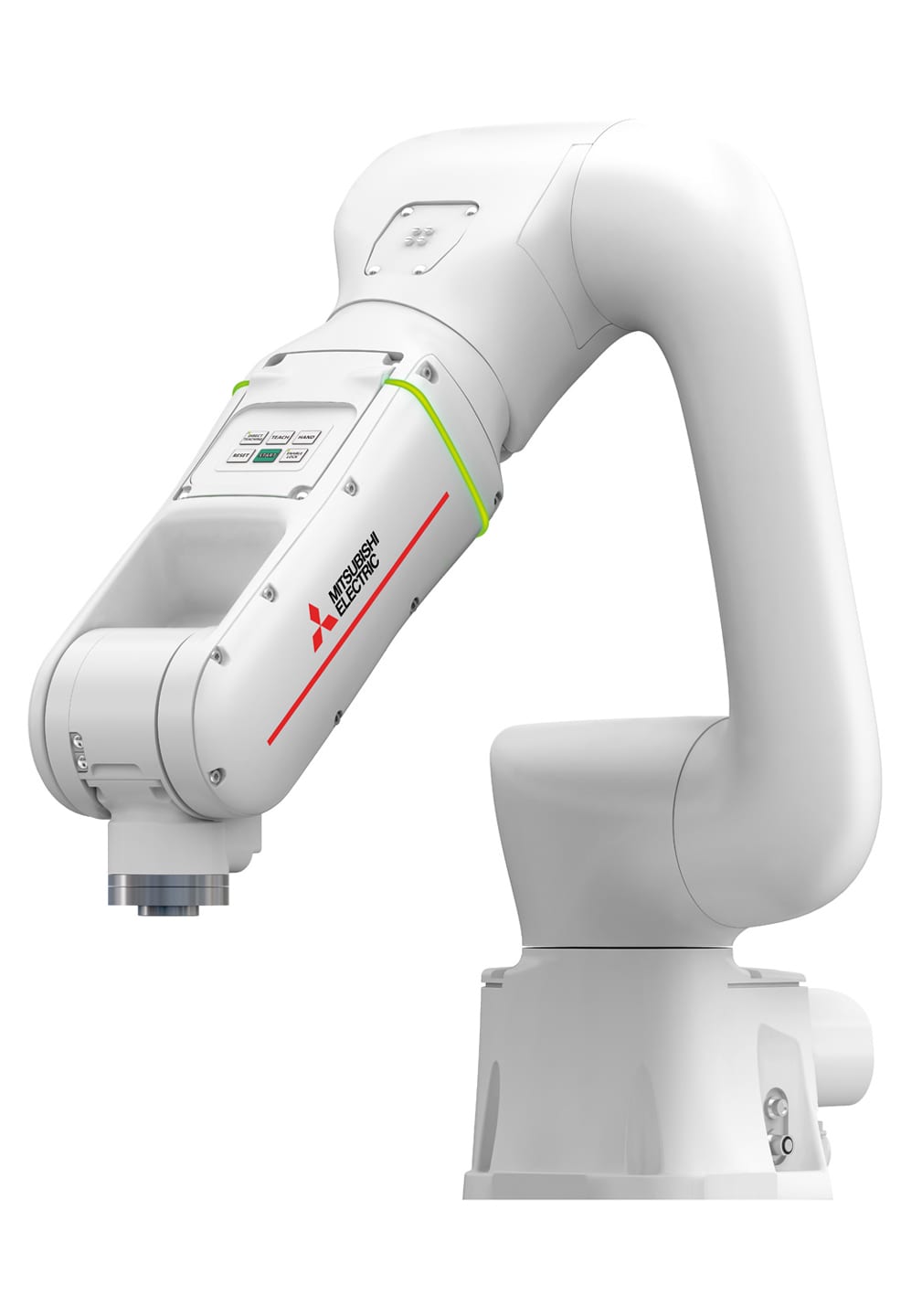 potteries, education, and research. The company proudly offers intelligent solutions of superior quality with highly rigid arms that enable high-speed and high-precision operations to support factories, arrange optimization, and be one step ahead of other manufacturers.
potteries, education, and research. The company proudly offers intelligent solutions of superior quality with highly rigid arms that enable high-speed and high-precision operations to support factories, arrange optimization, and be one step ahead of other manufacturers.
The ‘MELFA-FR’ series provides new, more intelligent solutions that underpin ‘next-generation adaptive manufacturing’ and offer a simpler approach to advanced and flexible production. With these key features – ‘intelligence’, ‘integration’, and ‘safety’ – the MELFA-FR Series of robots can handle all automation needs virtually.
From design to start-up, operation, and maintenance, the MELFA-Smart Plus delivers advanced intelligent functionality. Inserting a MELFA-Smart Plus card into a robot controller enables a multitude of intelligent functions. Temperature compensation, calibration assistance, coordinated control, and predictive maintenance are just some of the features that the MELFA-Smart Plus offers.
Maisart AI technology
Mitsubishi Electric has developed a fast force-feedback control algorithm for industrial robots using its Maisart (Mitsubishi Electric’s AI that creates state-of-the-art technologies) proprietary artificial intelligence (AI) technology, resulting in low-tolerance precision tasks to be performed with fewer trials and in less time compared to human-supported robot assembly. In company-conducted tests, this algorithm shortened assembly insertion times by around 65 percent without requiring the robots to move violently. Mitsubishi Electric India foresees that this algorithm can improve the efficiency of robotic tasks for assembling electric components such as printed circuit boards and connectors and inserting mechanical parts.
At this time, when interest in human-implemented cell-production systems is increasing, automatic-production systems that use industrial robots are also showing great promise in the developed and the developing countries where we see that humans are being promoted to the planning and ideation part, and repetitive tasks are efficiently being managed by industrial robots that are proving to be a good combination for humans. Until now, however, automatic systems for precision assembly and insertion operations have required programming and parameter adjustments by skilled personnel to achieve the flexibility of human-implemented assembly processes. Such requirements add to assembly costs and time, which manufacturers have been looking to reduce.
Mitsubishi Electric's Maisart AI technology, the new fast force-feedback control algorithm, shortens assembly time and eliminates violent movements by assembly robots. The technology allows parameters for tasks such as velocity to be adjusted quickly and precisely. In particular, high-precision force-sensor data can be incorporated without stopping the robots. Conventionally, robots are stopped prior to introducing force-feedback control, but Mitsubishi Electric India’s new algorithm eliminates this step.
Collaborative Robot ASSISTA
One of the most prominent applications of adaptive automation is in collaborative robotics. Traditionally, robots used to be operated within fenced enclosures, separated from human workers due to safety concerns. However, collaborative robots or cobots are designed to work alongside humans in shared workspaces. The modern cobots do not require any complex programming languages. For example, Mitsubishi Electric’s Collaborative Robot ‘ASSISTA’ can be programmed with a simple tablet supporting the advanced automated and digitalized era.
In conclusion, the evolution of industrial robots towards adaptive automation represents a paradigm shift in manufacturing. It heralds a future where robots are not just tools but intelligent collaborators and contributors, capable of navigating the complexities of modern industry with agility and efficiency. While challenges remain, many potential benefits like increased productivity, flexibility, and safety are compelling enough to amplify adaptive automation. This new era of adaptive automation is beneficial for the Manufacturing industry as it modifies the interaction and allocation of tasks between humans and robots, and the human decides the level of automation as and when required. As we stand on the verge of this transformative era, one thing is clear: The robots of tomorrow will be anything but rigid. They will be adaptive, autonomous, and poised to shape the future of industry in ways we are only beginning to imagine.
 |
Neelesh Chipade Product Manager Servo, Motion and Robotic Solutions Mitsubishi Electric India Pvt Ltd |



 Facebook
Facebook.png) Twitter
Twitter Linkedin
Linkedin Subscribe
Subscribe